| Å@ |
P&P (B) Biomaterials
& Biomechanics Project (1999-2000) |
Research
Members:
T. Murakami, Y. Murakami, S. Hirokawa, A. Takahara, Y. Sawae,
Y. Nakanishi,
K. Nakashima, H. Miura, K. Koyano, Y. Matsushita
Aims
(1) Elucidation of the various important facts such as the relation
between mechanical properties and structure,
and the role of mechanical stimuli on the remodeling of biological
tissues.
(2) Evaluation of actual performance of biomaterials and medical
devices such as joint prostheses and dental implants
(3) Optimum design of medical devices and implants
(4) Construction of mutual information network
Research
subjects
(1) Measurement of mechanical properties
and elucidation of remodeling process in biological tissues
(a) Analyses of microstructure of trabecular bones by means of
X-ray micro-CT
Ultra-micro-indentation test of cortical and mandibular bones
(b) Analyses of three-dimensional deformation and stress distribution
in a computationa model of human ligaments
Evaluation of mechanical properties of ligaments in two-directional
tensile tests
(c) Measurement of surface topography by means of AFM (atomic
force microscopy)
Deformation of articular cartilage and chondrocyte in compression
(d) Changes in bone remodeling by loading condition
Influence of mechanical stimuli on resorptive activity of osteoclast
(2) Evaluation of performance and
biocompatibility of biomaterials and implants in simulated biological
environments
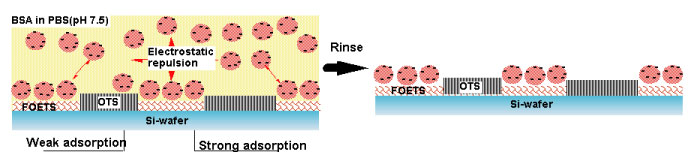
(a) Evaluation of adsorption of proteins, lipids and cells on
biomaterials
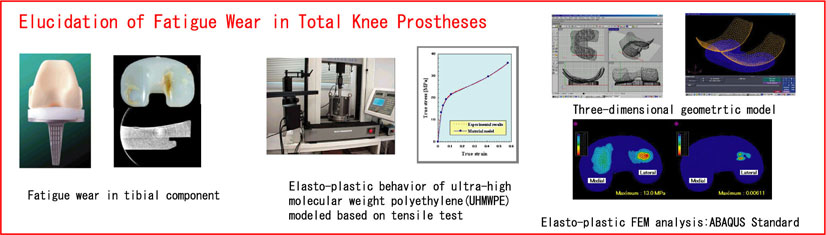
(b) Evaluation of artificial joint materials and joint prostheses
in multi-directional sliding testers and simulators
Contact stress analyses of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene
by finite element method
Application of polyvinylalcohol (PVA) hydrogel as artificial
cartilage
Clinical evaluation of joint prostheses
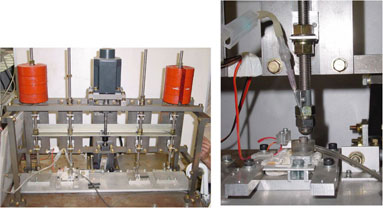
(c) Evaluation of mechanical performance of dental implants
Evaluation of the loosening of screw for dental implants in masticatory
simulator.
|